The crab with 8 legs and 2 claws has become an animal that is close and familiar to humans because of its nutritional and economic value. The world of crabs has many interesting things that people need to discover. This article, Toplist brings to you interesting facts about crabs that you may not know.
Description Information
The suborder Crab or true crab (scientific name: Brachyura) is a group containing crustaceans, the body is wider than the length, soft shell, ten articulated legs, the forelimbs evolved to become two claws, The bony shell covers the flesh, the abdomen is flattened below completely covered by the thorax. Crab animals are abundant in all seas and oceans. There are species that live in rivers, streams, and fields, such as species in the family Potamidae or family Crab (Parathelphusidae) and some species that live on land (family Gecarcinidae). The head of the crab and the body are joined together into a block with an outer shell.
The common names of species in this suborder in Vietnamese are quite diverse, such as crabs, sedges, crabs, damselflies, ram, scads, crabs, scads, etc., but these names do not seem to be the same names. monophyletic grouping from the point of view of modern phylogenetics but solely based on their morphology or habitat. Currently, it is estimated that there are close to 6,800 species.
The nomenclature "Brachyura" means "short-tailed" (Greek: βραχύς / brachys = short,[3] οὐρά / οura = tail), indicating that these species have a "tail" (actually ventral) part. very short, lying underneath and often hidden by the thorax.

Structure of crabs
The cephalothorax: The head and thorax in crabs are attached to each other, the boundary between the segments is not clear. Depending on the appendage carried on it, you know the number of segments formed. The head consists of 5 gill vertebrae, antenna and mouth appendages. The thorax consists of 8 segments bearing the jaws and the crawling legs. The dorsal surface of the cephalothorax is covered in cephalothorax (crab shell). The anterior edge of the cephalothorax has two eye sockets with two eyes located on the pedicle. Between the eye sockets, each anterior edge of the cephalothorax has 9 consecutive spines. The upper surface of the cephalothorax is divided into small regions separated by distinct grooves and ridges. Anterior is the forehead area, next is the stomach area separated by two ridges. Next is the heart area, after the heart area comes the intestinal area. On either side of the stomach is the liver. The outermost is the gill region. The ventral surface of the cephalothorax has ventral plates. The ventral plates form a concave center in which the abdomen folds in. In females, there is a pair of perforated birth holes located in the third abdominal plate, which is covered by the folded abdomen.
Abdomen: The abdomen consists of 7 segments with reduced appendages located under the cephalothorax (commonly known as the crab bibs) to make the crab shorter and compact to help the crab crawl. The abdomen in female crabs and male crabs is different. In sexually immature females (before the molting period, the abdomen) is slightly square (commonly called the square bib crab, the female crab). After molting, the bib becomes round (pregnancy bib) and the large bib size covers most of the abdomen, head and chest. The abdomen of the male crab is narrow, transversely narrowing posteriorly, has a triangular shape and also fits in the concave part of the ventral plates of the cephalothorax, in females the abdominal segments I, II and VII are synovial. the lateral segments, the others are immobile, the ventral legs are forked to turn into bundles of bib hair for the eggs to be laid on to develop. The anal opening is located at the end. In males, the abdominal segments I, II, V and VI are dynamically articulated with the lateral segments. The ventral legs degenerate into a pair of copulation spines, the anal opening at the end.
Subsections:
Mandibular I: consists of the base of the two leaves. The top of the two leaves are hairy… The inner branch of the apex is thin plate consisting of two hairy segments on the inner edge.
Mandibular II: consists of two-leaf base: blade-shaped inner leaf, hairy head; outer leaves are broad and hairy.
The base of the jaw I: consists of the base of two leaves: the inner leaf is small and hairy on the head, the outer leaf is broad at the tip and the outer margin is short hairy. The apex consists of two branches: the inner branch is flag-shaped, the inner edge has many long hairs, the outer branch consists of 3 segments. At the base, there is also a thin sheet of chitin in the shape of a rice leaf with long silk in the direction of the outside and back, called the gill of the water.
Foot jaw II: consists of many small root parts, the top has two branches, the inner branch has 5 segments, the inner edge has many hairs, the outer branch has 3 segments. The outside from the base part has a feather-shaped joint, and the outermost at the bottom has a water gill.
Mandibular foot III: very strongly chitinized, including the base of two segments. The apex has two branches.
Chest legs: 5 pairs. The first pair develops a large head with clamps (crabs). In males the two pincers are markedly different in size, usually the right one is larger than the left one. Crab claws are both for catching prey and as an organ of self-defense and attack powerful enemies. The 2nd, 3rd, 4th pairs of legs are cow's feet with 5 segments, the last one has sharp claws. The fifth pair of legs is shaped like a plate that turns into rowing, which is the main driving force when crabs swim.
Belly legs: In female crabs, there are 4 pairs of ventral legs, from the first abdominal segment to the fourth abdominal segment, which turns into an egg-keeping organ. The ventral legs are similar in structure, consisting of a basal segment and the apex consisting of two thin leaf-shaped branches covered with long hairs, the inner branch is segmented, and the outer branch is unsegmented. In male crabs, only the first and second ventral legs are left, which turn into copulation legs. The root part consists of 3 segments, the top only has the inner branch, not segmented.

Internal structure
Cut off the upper surface of the cephalothorax (crab shell), remove the upper covering, and see that the internal organs of the crab are located in the cephalothorax corresponding to the positions of the areas on the crab shell. Lying on the middle axis anteriorly is the stomach, then to the heart, finally the cecum mass. The two sides of the stomach are masses of liver glands, the pancreas above the body can see the gonads. Lying under the hepatopancreas, in the gill chamber are the articular gills, one end attached to the appendage root, the other free in the gill chamber.
Digestive system: The oral cavity on the ventral surface connects to the short esophagus, located along the dorsal axis of the abdomen, and enters the stomach. The stomach consists of two compartments: the epigastrium, which has a sharp chitinous mill, and the hypogastrium, which is separated from the epigastrium through the stoma. From the two sides of the hypogastric cavity, there are two hypogastric cecum located above the hepatopancreas mass. The hypogastric cavity communicates with the intestine and runs posteriorly into the abdominal cavity and ends with the fifth anal opening at the end of the abdomen. In the first part of the intestine, there are two long intestinal cecum. The hepatopancreas mass is very developed, filling the anterior part of the cephalothorax, including many fibrous lobes.
The circulatory system includes: Hepatopancreas, Heart, Crushed stomach, vas deferens, testicles, cecum, intestines, gills, intestinal tubes, vents, and anus. The blood of the crab is colorless and transparent. The heart of the crab has a pentagonal shape, located behind the stomach in a thin and transparent heart capsule, with 3 pairs of heart holes: 2 pairs on the dorsal side, 1 pair on the abdomen. From the heart, two large arteries go forward and behind the body, enter the organs, then follow the sinus openings to focus on the gills, in the gills, the blood takes out CO2 and receives O2, and then follows the vascular tubes back to the heart.
Respiratory system: Consists of 8 pairs of large and long gills attached to the base of the appendages located in the gill cavity on either side of the cephalothorax. There are also water bottles. Joint gills consist of a longitudinal axis and two rows of gill leaves arranged consecutively along the gill axis. External water enters the crab's gills through the suction slit located under the crab's claws, the gills stir in the gill cavity causing water to flow continuously and the water exits through the slit under the second tentacle. Thus, the water flow will run continuously in the gills. Water passes through the gills, the blood vessels of the gills receive oxygen and release carbon dioxide into the water. When the crabs land, a certain amount of water is retained in the gill cavity to help the crab continue to breathe and live for a long time.
Genitourinary system: In males the pale white seminal vesicles are located on the hepatopancreas mass. The vas deferens are long, coiled, and emptied into the male genital opening on the ventral surface. In females, the ovary changes color depending on the stage of sex cell development. Ripe eggs are orange-red. The large short oviduct drains directly into the female genital opening on the ventral surface near the base of the crab's third legs.
Nervous system: The feature of the nervous system in crabs is the phenomenon of high concentration of the thoracic and ventral ganglia. In the first part, the nervous system consists of the cerebral ganglia and the esophageal nerve region. On each branch of this region there is a small ganglion, known as the sympathetic ganglia. The esophageal nerve ring connects to the thoracic and ventral ganglia, where many nerves travel to the thoracic appendages and internal organs. There is a small hole in the middle of this nodule. Behind the thoracic ganglion block, there is a pair of long abdominal nerves that enter the abdomen. In the anterior and posterior brain regions, on the thoracic ganglia, the optic ganglia and the eye stalk, there are also neuroendocrine glands capable of secreting hormones that control the process of molting, gametogenesis, and male differentiation. , female, color change : molting and growth control gland, growth inhibitory gland, molting.

Sense organs
Crab sense organs are well developed. The organs of touch and taste are in the form of sensory filaments concentrated in antennas and appendages. These filaments communicate with nerve cells located under the epithelium. The balance organ is the cystic flask, which has the form of a depression located at the base of the antennae I with many sensory fibers, which contain many small grains of sand taken in from the outside through each molt. In crabs, there are organs for broadcasting and receiving sounds in the joints of the legs.
The crab's visual organ is compound eyes. Each compound eye is structured as follows:
The outermost is the transparent horny membrane secreted by the keratinocytes.
Beneath the horny membrane is the cone-shaped vitreous, surrounded by pigment cells.
In the innermost part is a cluster of photoreceptor network cells, arranged in an asterisk pattern along the longitudinal axis, surrounding a long rod-shaped cylinder, which is secreted by the reticular cells.
The head in the reticular cell communicates with the nerve.
All of these nerves form the optic nerve, which travels to the optic nerve ganglia, along the length of the eye stalk.

The process of molting of crabs
During the period of development from larva to adult, crabs have to undergo many molts. Crab and other crustaceans have a body covered with a chitinous exoskeleton. Thanks to the absorption of calcium and calcification, the shell of the crab is very strong. While the shell is fixed and crustaceans grow over time, the shell must be replaced periodically during metamorphosis (from free-swimming larva to adult) or monogamy. simply when they grow out of the shell.
Before molting, a crab usually absorbs calcium from the old shell, then secretes enzymes to separate the old shell from the skin or cuticle. This skin will be surrounded by a new shell, which is softer and thinner than the old one, NOAA said.
A day before molting, the crab begins to absorb seawater, and its body begins to swell like a balloon. This helps them to expand the old shell and split a small fissure running throughout the body. The crab will then withdraw the old shell by pushing out and retracting the body parts several times, until the front legs are retracted and completely detached from the old shell. The process of changing a new shell of a crab usually takes about 15 minutes.
To develop, a crab must go through many metamorphic molts. The time between molts can vary depending on the stage. Larvae can molt every 3-5 days. Large crabs molt to develop usually every fortnight to once a month. During molting, crabs may lose some parts such as legs and claws, but can regenerate these parts in the next molt.

Reproductive behavior of crabs
Before molting, the male and female crabs will mate for about 2 to 10 days. Male crabs (usually larger than female crabs) use their crawling legs and claws to hold the female crab on the dorsal side. It carries the female around all the time, sometimes for 3 to 4 days or more. When the female is about to shed her shell to mate, the male will leave the female and stay close; When the female has just finished molting, the male immediately holds the female close to the abdomen and takes off the female's bib to mate.
Mating time can last from about 5 hours to a whole day. The male will then let go of the female crab, but will still walk beside her to protect the female crab. After mating, the seminal vesicles are kept in the sperm receiving part of the female crab for a long time to fertilize the female crab's eggs. During the breeding season, the female crab can lay eggs 1-3 times and is fertilized by sperm received around the beginning of the breeding season. Our experiments showed that brick crabs caught and reared in a cement tank (without male crabs) from July to October laid eggs 3 times and all eggs developed into larvae.
After mating, female crabs will continue to grow and mature, lay eggs and fertilize. When laying eggs of female crabs lying on the bottom, using her legs to cling to the bottom, the cephalothorax is raised, the abdomen is opened, the abdominal legs are erected, the eggs are matured through the fallopian tubes and have been fertilized with sperm. spermatozoa from the sperm sac.
The eggs laid are contained in the female's abdomen with 2 membranes; The outer membrane absorbs water and swells. Between the two membranes there is mucus. Thanks to the movements of the abdomen, the eggs cling to the hairs of the abdominal legs and due to the effect of the external force of the outer membrane of the eggs, stretch out into "egg stalks", making the eggs stick to the hairs of the abdominal legs but remains "free" and the eggs do not stick together. The female crabs that hold the eggs are called egg crabs, the eggs that are hugged by the female crab continue to develop until they become new larvae that leave the crab's abdomen, so they are also called "baby crabs".

The crabs with the most bizarre appearance
The world of species is very diverse in both shape and size. Some are very scary, some are colorful, and some are very bizarre.
Halloween Crab. This species has many colors. Halloween crabs live mainly in the waters of Mexico, Central America and possibly as far as Peru. They often roam the forest and eat tree leaves or seeds. This species is nocturnal. Although living mainly on the ground, this crab species has to return to the country to lay eggs.
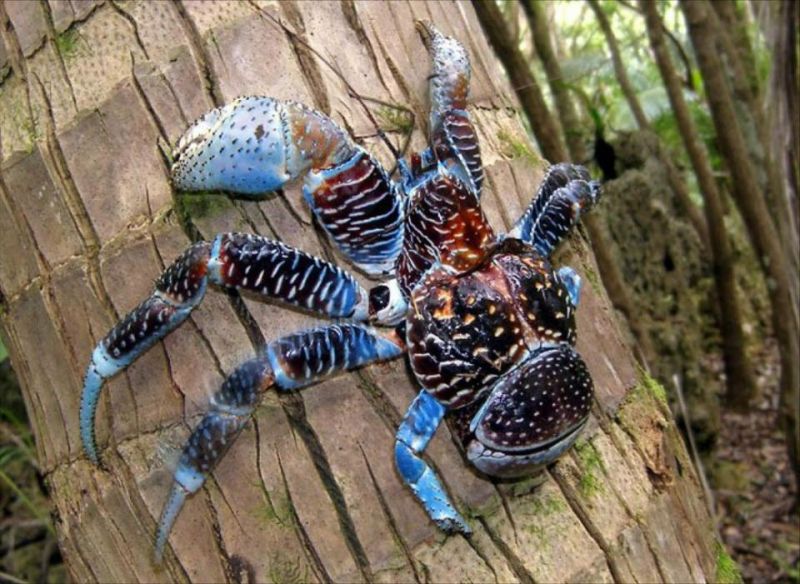
Coconut crabs. It is one of the largest terrestrial arthropods. It weighs 4.1kg. Coconut crabs live mainly on islands in the south Pacific Ocean. They eat nuts, seeds and occasionally coconuts. They are quite a "bizarre" species when they have a special respiratory system, not a bib, not a lung, but something between these two parts. Their sense organs are more like those of insects than of crabs.
King of thorns crab. The whole body of this crab is covered with a layer of spines, which both help them camouflage and help them protect themselves from predators. This species lives at a depth of 730m under the sea. They eat starfish, other crabs, and droppings from above.
Brown box crab. This is also a type of king crab. They have a strange way of breathing: when the front claws are passed through the shell, the V-shape on the claws along with the adjacent legs will form a small hole, allowing water to flow into the lungs, under the sediment.
Soft coral crab. These "monsters" have excellent camouflage ability when living with soft corals and eating plankton.
Zebra tiger crab. This species lives mainly in the Indian Ocean, Pacific Ocean, Australia. This species has a peculiar shape, with dark, white markings resembling a zebra.
Orangutan crab. Belonging to the family of spiders and crabs, this strange little creature looks very much like an orangutan. They have thick orange fur, 2 long legs that look like orangutans' hands.
Porcelain crab. These crabs are not really crabs, they are an evolved shrimp that looks like a crab. They are quite fragile and break easily. This type often loses its legs when fleeing from an enemy and these legs are later regrowed. This species feeds on the mucus of the seaweed plants, helping them to clean themselves, while the algae protect the crabs from predators.

Crab food
Crab eat mainly zooplankton. Until now, most of the crab farming households use fresh animal food as the main source. The main foods of crabs are: shredded fish, crabs, fish heads, don, lead, mussels, snails, fish, shrimp, cuffs, civets...
Plants include: vegetables, tubers, water hyacinth, potatoes, cassava, rice bran residue, etc.
Live food: Includes animals that are still whole, alive or dead, but with fresh meat. Do not use animal meat that has been spoiled and salted animal meat that is not able to wash off the salt. Animals and meat used as food for crabs include:
Fresh fish: usually use marine fish such as Son fish, Linh fish, mouse pin, sea fish, etc. Molluscs: including molluscs such as don, lead...
Crustaceans: mostly inexpensive shrimp and crabs.
Other animals: usually make use of the meat of cheap animals that are not used as food for humans, and meat scraps of food processing enterprises such as fish, shrimp, squid...
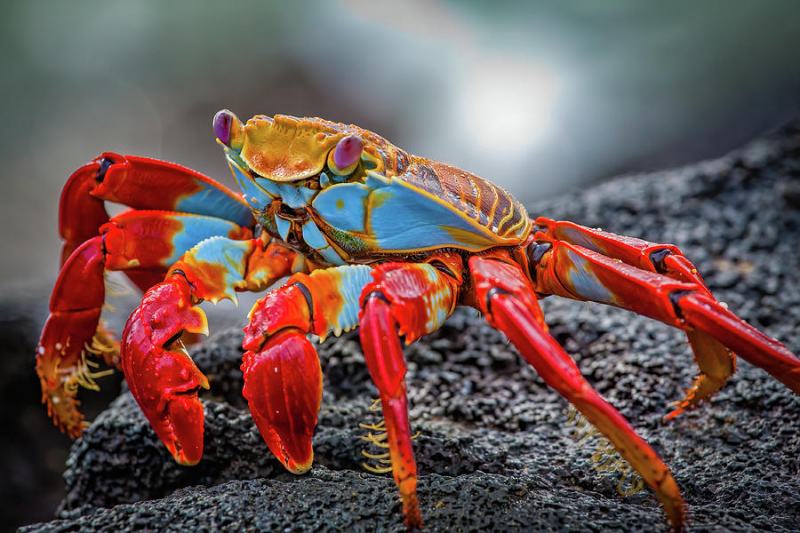

The most delicious crabs today
Hong Kong Hairy Crab: Hong Kong Hairy Crab is also known by another name, Shanghai Hairy Crab. Every year, around September - October is crab season. Compared to other crab species, hairy crabs are much smaller in size, each weighing about 150-200g and covered with a rough outer layer of hair. Despite its small size, hairy crab is considered one of the most delicious crabs today and is a favorite dish of the upper class. The crab meat is firm, white, smooth, and naturally sweet, while the crab bricks are greasy but not greasy. Therefore, hairy crabs are called the "king" of crabs by many seafood believers.
Australian Crystal Crab (Australian Snow Crab): Australian Crystal Crab, also known as Australian Snow Crab, is a crab that is caught naturally from the pristine waters of the western region of Australia. The crab shell is white, big and clear like a sparkling crystal in the bottom of the blue ocean. To catch this crab, fishermen have to dive deep to the bottom of the ocean, so the price of this crab is very expensive. Besides, Australian Crystal crab is also favored by many people because of its delicious taste, firm meat, and natural sweetness that few other crabs can match.
Australian Tasmanian Crab: The Australian Tasmanian crab is a species of crab native to the waters of Tasmania in the south of Australia. The crab has the same shape as the sea crabs of Vietnam, but the size is about 10 to 20 times larger. Adults can weigh up to 10kg. With a unique taste, delicious brick, crispy meat, natural sweetness, Australian Tasmanian crab is loved and bought by many seafood lovers.
Alaskan crabs: Alaskan crabs are crabs native to the waters of North America at depths of 200-400m. Crab has a large size, rounded body looks almost like a giant turtle or beetle. The head of the crab is hairy, long and slightly downward. Crab has a special flavor, greasy, delicious crab meat, firm brick. Therefore, despite the expensive price, king crabs are still loved and hunted by many people.
Alaska Ruby Crab: Alaska Ruby Crab is a species of crab that lives in the North American waters of the state of Alaska. Ruby crabs also belong to the same family as King Crab, so they have a relatively similar appearance. However, King Crab's legs are much longer than Ruby's legs. Ruby crab meat has a natural white color, a sweet taste and is very crunchy.
King crab is one of the famous specialties in some remote islands and seas of the South Central Coast in our country. The crab has a large size and a very special shape with an elongated appearance and a red-pink shell like boiled shrimp. The claws and legs are short, the shell is large and similar in shape to the letter U with many antennae around. Each adult crab can weigh up to about 1kg. King crab meat has a superior flavor compared to other sea crabs in terms of deliciousness, sweetness, crunch, and fat. Therefore, this species of crab is hunted by many seafood believers to prove its "gourmet".

The most dangerous poisonous crabs today
Devil's face crab: Devil's face crab is a common toxin-containing sea crab stretching from the waters of Da Nang to Vung Tau, often living in shallow reefs and low tide. Devil face crabs are quite compact in size in the palm of the hand, on the shell there are many convex, flattened lumps on the outside of the shell and eye-catching colors, unlike other sea crabs. In the meat and shell of the devil crab there is a large amount of toxic substances for the nervous system such as Tetrodotoxin and Saxitoxin, which can be fatal to humans if accidentally ingested even in extremely low doses. The poison of the devil face crab is mainly in the meat, eggs and many substances in the meat of the claws and legs. These toxins are extremely toxic, similar to the poison in puffer fish, directly affecting the nervous system, inhibiting respiration. Currently, there is no antidote for the Saxitoxin in the devil face crab. If people are poisoned, if they are not treated in time, the risk of death is very high, it is important to stay away from this dangerous crab.
Sea rock crab: Sea rock crab is a large land crab, has a dark purple shell, long legs and rather short legs. They are nocturnal animals, sheltering in burrows during the day and feeding on plants. When ripe, sea rock crab turns brick color. Sea rock crabs also contain dangerous poisons like devil face crabs. The characteristic to recognize them is that the cephalothorax has a semicircular shape, about 30mm at the longest and about 40mm at the widest, covered with granular protrusions.
Sea rock crab is rare and very difficult to catch, the meat has a sweet taste, so it has become a favorite specialty of many people. However, in the process of processing and using, if it is not cleaned of toxins, it will cause negative health effects and may leave unfortunate consequences as above.
Florida Crab: The identifying feature of this crab is the transverse elliptical cephalothorax. The dorsal surface of the crab shell is slightly convex but quite smooth. Crab has pale greenish blue streaks, mixed burgundy streaks, dark pincer toes. This type of crab usually lives in the sea from Da Nang to Khanh Hoa. In Da Nang, there was an unfortunate case of eating this Florida crab. Specifically, after boiling and eating Florida crab, the victim accidentally showed strange symptoms such as constantly vomiting and had to be taken to the emergency room immediately.
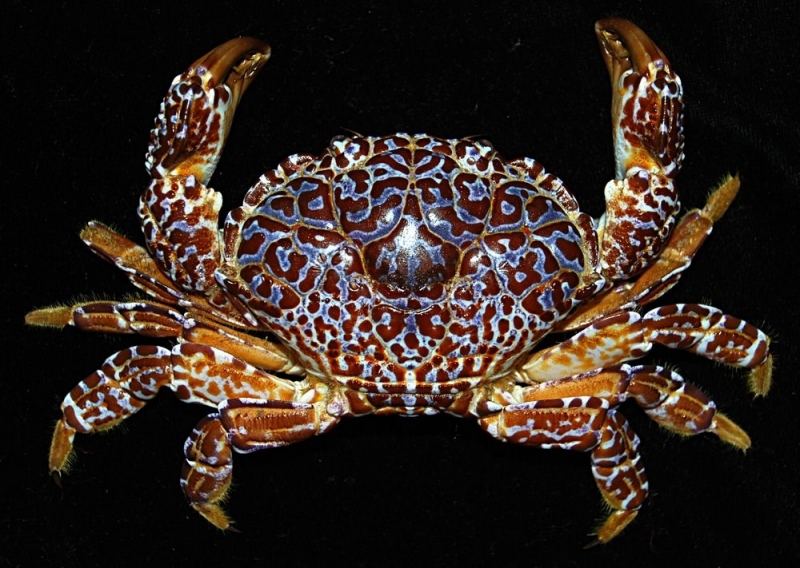

Arrow crab - Crab has legs 5 times longer than its body
Arrow crabs are notable for their legs up to 20cm long - 5 times their body length. The Blue Reef Marine Park in Newquay (UK) has just welcomed a very special new resident, an arrow crab. This crab has a body length of only 4cm, but their legs are up to 20cm long.
The scientists who first discovered these crabs called them arrow crabs because their heads are pointed and the eyes bulge outwards, which look a lot like the head of an arrow.
Arrow crabs usually live in coral reefs about 10m above the water in the western Atlantic Ocean, from the US down to Brazil and across the Caribbean Sea. Their food is mainly carrion of marine species, algae and plankton.
Their bodies also have a variety of colors, including yellow or cream with brown, black, or iridescent spots, ... to adapt to their surroundings. Their legs are usually red or yellow, while the legs are blue or purple.
The female arrow crab carries eggs under the abdomen until the eggs hatch and the larvae after hatching will swim with plankton on the surface of the water. These larvae then return to the reefs and undergo a series of shedding before becoming adults.

Pacific spider crab - car-long crab
The undersea world is always mysterious and captivating. Despite modern science and technology, submarines are diving deeper and deeper, but they have not yet explored the ocean floor. Particularly for crabs, there are countless subspecies on the seabed. However, in the family of crabs, scientists note the Pacific spider crab is the largest known species in the world. This giant crab lives on the seabed on the Japanese side, so it is sometimes called the Japanese spider crab.
Because this giant, spider-like crab lives on the seabed, information about them is still a mystery, except that their meat is very fatty and nutritious, which is well known to gourmets. Scientists have calculated and concluded that spider crabs possess the longest legs among crustaceans. While field crabs only have a length of about 10cm from one tip to the other, an adult spider crab has a length of 4-5m on both ends, as long as a 4-seater car.
Its wobbly legs support a body about half a meter wide and weigh up to 20kg. People often call long-legged women as women, while sea crabs are the opposite. Male crabs have long legs, while female crabs have short legs. Even its claws are shorter than its legs.
Although spider crabs have a fierce, aggressive appearance, making the observer think of giant man-eating poisonous spiders in movies, they are actually quite gentle species. They take advantage of sponges or other creatures to disguise and evade opponents rather than find ways to defend themselves or attack back. Meeting enemies, they can only rely on hard shells, like turtles with their necks.

New species of "strawberry" crab found
According to AP, the person who discovered the new crab species is Professor Ho Ping-ho of the Taiwan Ocean University. He said that they are quite similar in shape to the crabs that live in the waters of Hawaii (USA), the Polynesian islands and the island nation of Mauritius (southwest of the Indian Ocean). However, the new species of crab possesses a shell shaped like a mussel and is about 2.5 cm long. The shell makes them different from the red crabs.
Wang Chia-hsiang, a leading crab expert in Taiwan, confirmed Professor Ho's findings.
Ho said he and his colleagues found two females of a new species of crab in the Kenting reserve, which is home to many marine animals. Two crabs were dead when the scientists saw them. Ho thinks they most likely died because a cargo ship ran aground near the reserve, causing the water to be polluted.
Crabs are omnivores. Their main food is algae. According to the Daily Mail, scientists have identified more than 5,000 species of crabs in the world.

Strange species of crabs completely inhabiting trees in India
Scientists at the University of Kerala, India, discovered a strange new species of crab, living in the trees in the forests of the Western Ghats, southern India. They are described in a paper published in the journal Crustacean Biology on April 3. The local Kani tribe knew about the existence of these particular crabs and helped the team find them. In recognition of their efforts, the crab species was scientifically named Kani maranjandu.
This is the first time scientists have discovered a species of crab that lives entirely in trees. Their homes are puddles of water in the hollows of trees, rather than on the ground like the usual crabs.
Little is known about Kani maranjandu crabs due to their shy nature. The Kani people taught researchers how to locate the animal by looking for wood chips and air bubbles pushed out of holes in trees. The Kani maranjandu crab has a purple-black shell and elongated legs that are well-suited to arboreal life.
Scientists say this is a very important discovery. Kani maranjandu crabs serve as indicator organisms in the field of ecology. Where there is a large number of crabs, it proves that the forest ecosystem is still good. Water-filled hollows in large trees are the habitat of this unique crab.

Above is the most useful information about crabs. Hope the article brings a lot of useful information for readers.